Egg Products
Eggs are the best protein money can buy, and they have many other valuable vitamins and minerals too.
Nutrient Content of a Large Egg
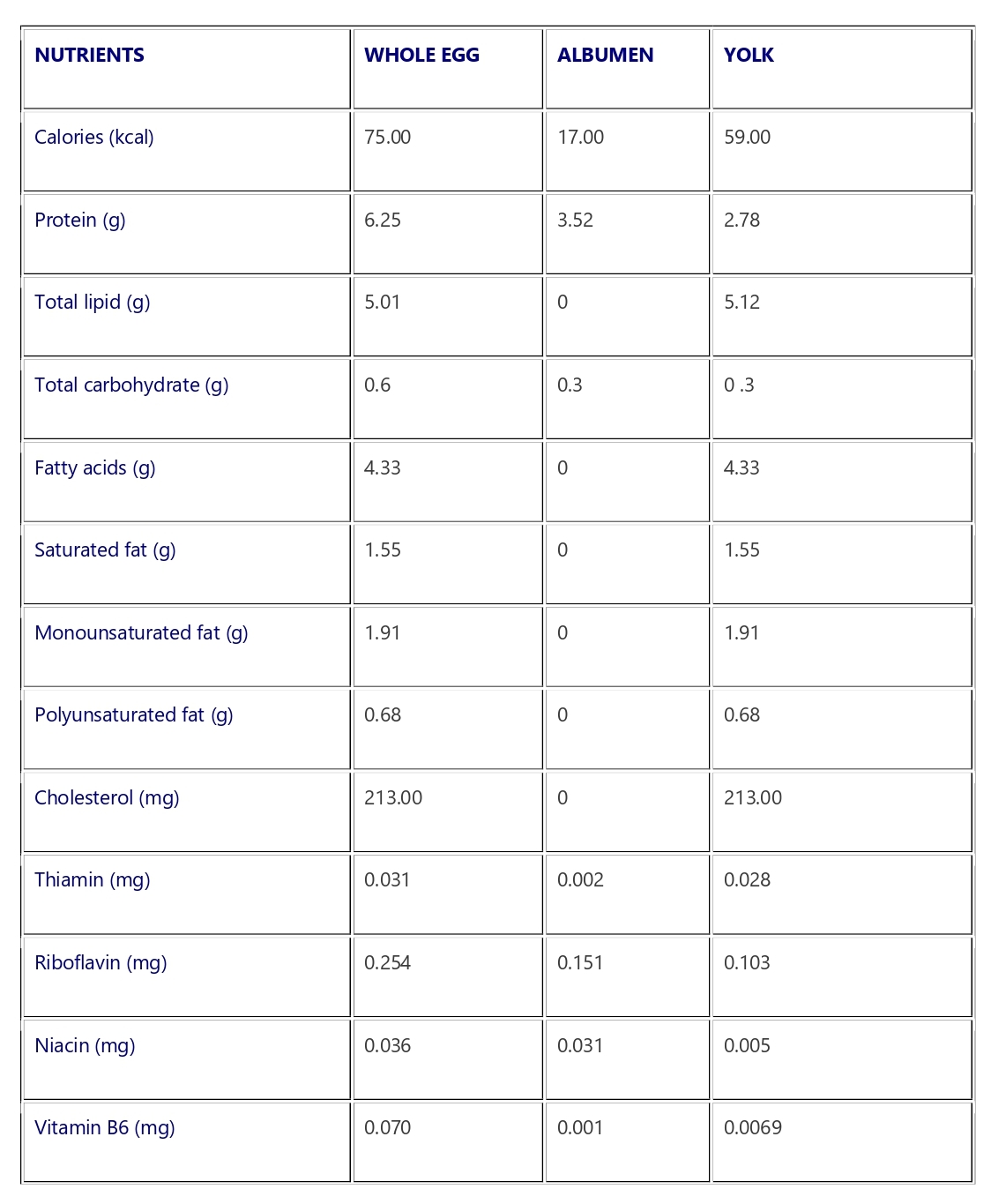
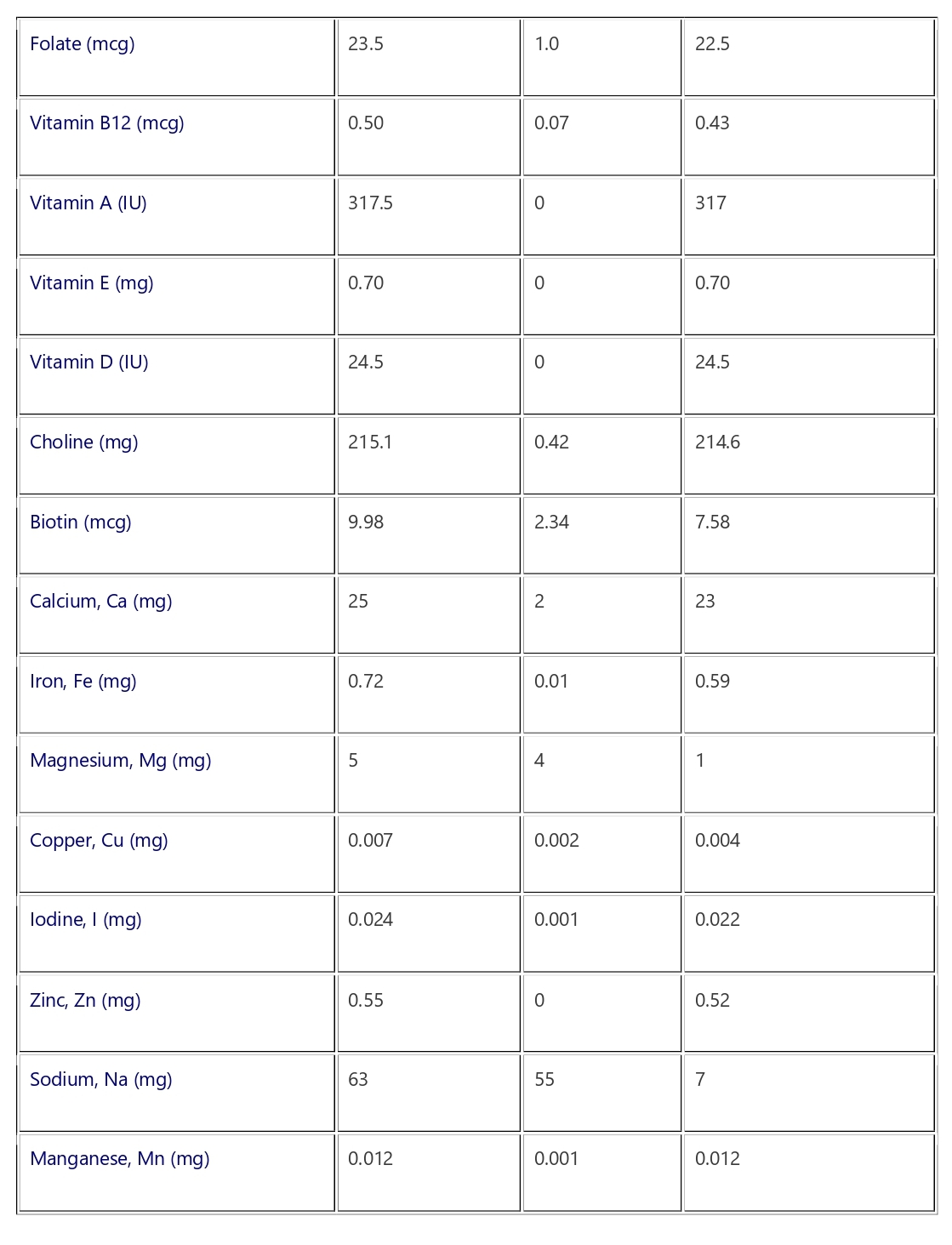
| NUTRIENTS | WHOLE EGG | ALBUMEN | YOLK |
| Calories (kcal) | 75.00 | 17.00 | 59.00 |
| Protein (g) | 6.25 | 3.52 | 2.78 |
| Total lipid (g) | 5.01 | 0 | 5.12 |
| Total carbohydrate (g) | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0 .3 |
| Fatty acids (g) | 4.33 | 0 | 4.33 |
| Saturated fat (g) | 1.55 | 0 | 1.55 |
| Monounsaturated fat (g) | 1.91 | 0 | 1.91 |
| Polyunsaturated fat (g) | 0.68 | 0 | 0.68 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 213.00 | 0 | 213.00 |
| Thiamin (mg) | 0.031 | 0.002 | 0.028 |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 0.254 | 0.151 | 0.103 |
| Niacin (mg) | 0.036 | 0.031 | 0.005 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 0.070 | 0.001 | 0.0069 |
| Folate (mcg) | 23.5 | 1.0 | 22.5 |
| Vitamin B12 (mcg) | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.43 |
| Vitamin A (IU) | 317.5 | 0 | 317 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 0.70 | 0 | 0.70 |
| Vitamin D (IU) | 24.5 | 0 | 24.5 |
| Choline (mg) | 215.1 | 0.42 | 214.6 |
| Biotin (mcg) | 9.98 | 2.34 | 7.58 |
| Calcium, Ca (mg) | 25 | 2 | 23 |
| Iron, Fe (mg) | 0.72 | 0.01 | 0.59 |
| Magnesium, Mg (mg) | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Copper, Cu (mg) | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.004 |
| Iodine, I (mg) | 0.024 | 0.001 | 0.022 |
| Zinc, Zn (mg) | 0.55 | 0 | 0.52 |
| Sodium, Na (mg) | 63 | 55 | 7 |
| Manganese, Mn (mg) | 0.012 | 0.001 | 0.012 |
The Egg: Functional Properties
- Foaming.
- Coagulation.
- Emulsification.
- Crystallization Control.
- Flavor Enhancing.
- Imparting Pleasing Colour.
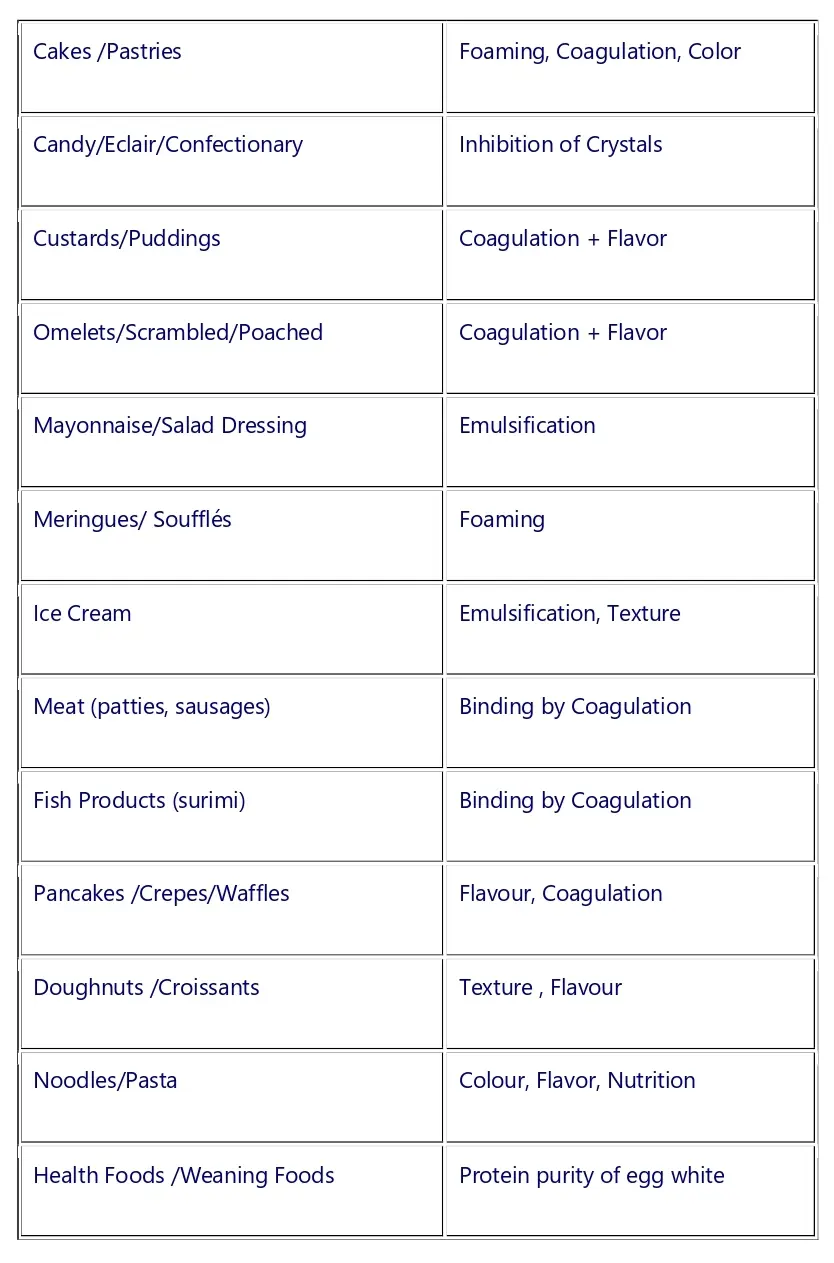
Use and Function of Eggs in food
| Cakes /Pastries | Foaming, Coagulation, Color |
| Candy/Eclair/Confectionary | Inhibition of Crystals |
| Custards/Puddings | Coagulation + Flavor |
| Omelets/Scrambled/Poached | Coagulation + Flavor |
| Mayonnaise/Salad Dressing | Emulsification |
| Meringues/ Soufflés | Foaming |
| Ice Cream | Emulsification, Texture |
| Meat (patties, sausages) | Binding by Coagulation |
| Fish Products (surimi) | Binding by Coagulation |
| Pancakes /Crepes/Waffles | Flavour, Coagulation |
| Doughnuts /Croissants | Texture , Flavour |
| Noodles/Pasta | Colour, Flavor, Nutrition |
| Health Foods /Weaning Foods | Protein purity of egg white |
Disadvantages of using Egg in Shell
1. Large labour force needed to break and separate eggs for getting the liquid. This is expensive.
2. Because of large labour force, human contact at many places is unavoidable. This is un hygienic.
3. Refrigerated storage space is essential to preserve the quality of shell eggs. This is expensive.
4. Losses by breakage because of handling during unloading and transporting to point of use.
5. Procurement has to be ‘use based’. We cannot take advantage of larger purchases at low prices.
6. Source of eggs is not known. Thus, the conditions in which the egg was produced is suspect.
7. Egg contents may not be standard in terms of color /fat/protein. This may need frequent recipe adjustment.
8. Egg contents may not be safe. Salmonella and other harmful bacteria are likely to be present.
9. Use of shell eggs is prohibited in flight kitchens and some institutional catering establishments due to fear of Salmonella or other pathogenic organisms.
10. Disposal of egg shells and waste liquid is a problem and leads to unhygienic conditions in a food processing factory. Pollution Control Authorities take a serious view of this matter.
11. Recipes using only egg white or only egg yolk lead to wastage of the other component.
12. There is a chance that egg shell particles are present in the final product leading to complaint from consumers.
Features of dried egg products
- Most convenient and economical form of eggs for transportation, storage and recipe formulation.
- Preservation is achieved without any additives. Microbiological deterioration is arrested by removal of moisture to below a level of 5%.
- Worldwide trend of about 8-10% growth in dried egg products compared to other forms of eggs.
Storage Requirements and shelf life of dried eggs
- Dried egg products should be stored in a cool & dry place.
- They should not be stored along with other items with strong odour.
- Shelf life depends on temperature of storage.
- Long storage at high temperatures (35 deg C) causes degradation of protein. This affects some functional properties.
- Store below 25 deg C to ensure shelf life up to twelve (12) months.
Reconstitution of Eggs from Egg Powder
- Whole Egg Powder: Add 3 parts of water to 1 part of powder by weight and mix to obtain uniform consistency.
- Egg Yolk Powder: Add 1.1 parts of water to 1 part of powder by weight and mix to obtain uniform consistency.
- Egg Albumen Powder: Add 7 parts of water to 1 part of the powder by wt and mix to obtain uniform consistency.
